STEP #04 - La scienza
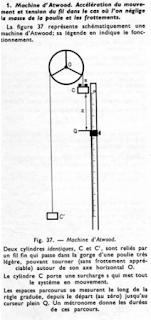
La macchina Atwood fu inventata matematico inglese George Atwood come esperimento di laboratorio per verificare le leggi meccaniche del moto con accelerazione costante.
Le leggi del moto di Newton sono tre leggi fisiche che hanno gettato le basi per la meccanica classica. Descrivono la relazione tra un corpo e le forze che agiscono su di esso e il suo movimento in risposta a quelle forze. Queste tre leggi sono state espresse in diversi modi, nel corso di quasi tre secoli, e possono essere riassunte come segue:
- Prima legge:In un sistema di riferimento inerziale, un oggetto rimane a riposo o continua a muoversi a velocità costante, a meno che non venga influenzato da una forza.
- Seconda legge:In un sistema di riferimento inerziale, la somma vettoriale delle forze F su un oggetto è uguale alla massa m di quell'oggetto moltiplicata per l'accelerazione a dell'oggetto: F = ma.
- Terza legge:Quando un corpo esercita una forza su un secondo corpo, il secondo corpo esercita simultaneamente una forza uguale in grandezza e opposta in direzione sul primo corpo.
ENGLISH VERISION
The Atwood machine was invented by the English mathematician George Atwood as a laboratory experiment to verify the mechanical laws of motion with constant acceleration.
Newton's laws of motion are three physical laws that laid the foundation for classical mechanics. They describe the relationship between a body and the forces acting upon it, and its motion in response to those forces. These three laws have been expressed in several ways, over nearly three centuries, and can be summarised as follows:
- First lawIn an inertial frame of reference, an object either remains at rest or continues to move at a constant velocity, unless acted upon by a force.
- Second lawIn an inertial frame of reference, the vector sum of the forces F on an object is equal to the mass m of that object multiplied by the acceleration a of the object: F = ma.
- Third lawWhen one body exerts a force on a second body, the second body simultaneously exerts a force equal in magnitude and opposite in direction on the first body
sitografia:
www.it.wikipedia.org/wiki/Macchina_di_Atwood
www.en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Newton_laws_of_motion
www.museovirtualefisicanievo.com/macchina-di-atwood
www.fondazionegalileogalilei.it/museo/collezioni/strumenti_scientifici/meccanica/schede_meccanica/macch_atwood
www.digilander.libero.it/ricciardi/www.na.infn.it/Museum/schede/313b
www.americanhistory.si.edu/collections/search/object/nmah_1865665
www.physlab.uniurb.it/Collection_Mechanics04.html
www.museovirtualefisicanievo.com/macchina-di-atwood
www.fondazionegalileogalilei.it/museo/collezioni/strumenti_scientifici/meccanica/schede_meccanica/macch_atwood
www.digilander.libero.it/ricciardi/www.na.infn.it/Museum/schede/313b
www.americanhistory.si.edu/collections/search/object/nmah_1865665
www.physlab.uniurb.it/Collection_Mechanics04.html


Commenti
Posta un commento